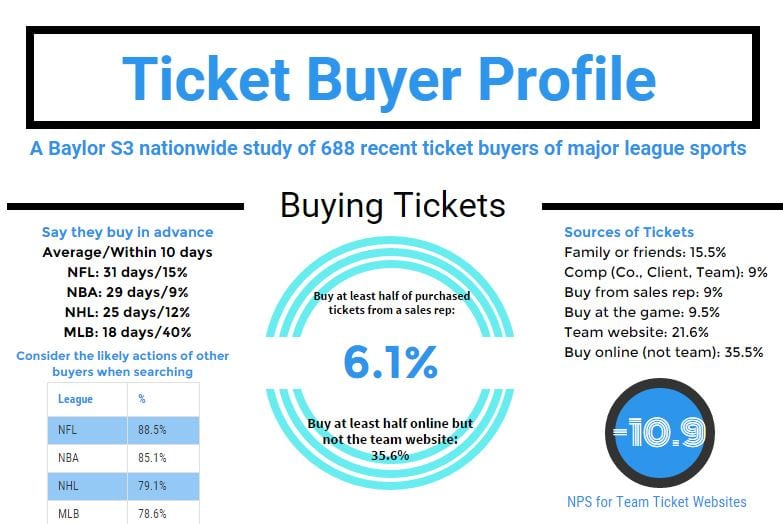
by Kirk Wakefield – June 2017 What is Grit? Angela Duckworth made an industry out of her own passion and perseverance toward a long-term goal–her definition of grit–and measuring it in others. Controlling for other factors (SAT scores, IQ, self-control, and the Big 5 personality traits), she and her colleague’s research[ref]Duckworth, Peterson, Matthews & Kelly…Continue Reading Does Grit Lead to High Performance in Sales?
Does Grit Lead to High Performance in Sales?